What Are the Best Ways to Avoid Gingivitis?
Gingivitis is a common yet often overlooked condition that affects the gums and can lead to more serious dental problems if left untreated. This inflammation of the gum tissue can cause redness, swelling, and bleeding, making it an early warning sign for gum disease. Fortunately, gingivitis is preventable with the right habits and regular dental care. In this article, we will explore the best ways to prevent gingivitis, including proper oral hygiene practices, dietary recommendations, and lifestyle changes to keep your gums healthy. Understanding how gingivitis develops and taking proactive steps can help you maintain a brighter, healthier smile for years to come.
Key Takeaways
- Brush after every meal: Regular brushing, especially after meals, is key to preventing gingivitis.
- Floss daily: Flossing helps remove plaque and food particles from between your teeth, reducing the risk of gum inflammation.
- Maintain a balanced diet: Proper nutrition supports your immune system and helps protect your gums.
- Quit tobacco: Tobacco use increases the risk of gingivitis and other gum diseases.
- Regular dental checkups: Regular visits to your dentist help catch potential issues early, preventing gingivitis.
Why Gingivitis Happens and Why You Should Care
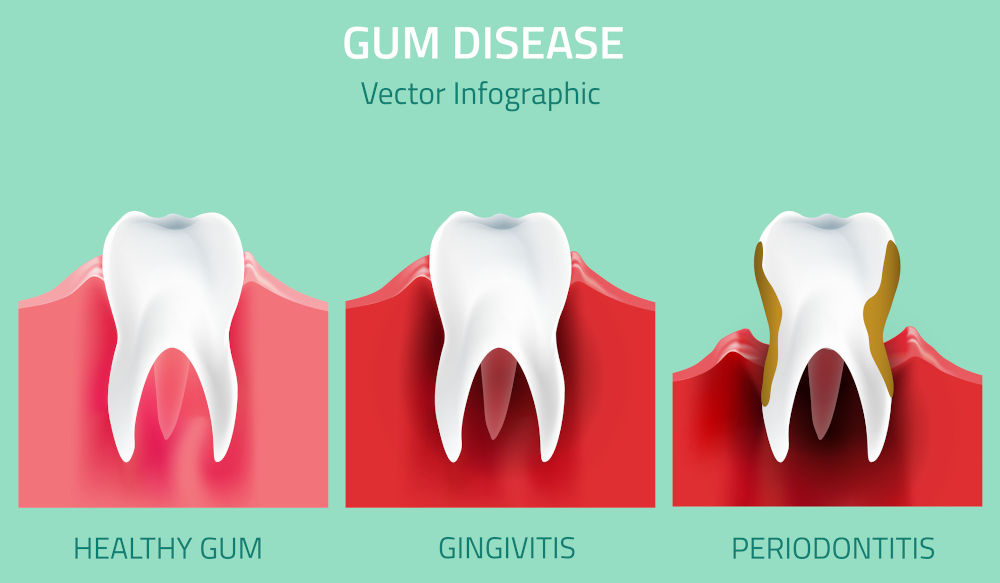
Gingivitis is a common but serious condition that can lead to gum disease if left untreated. It is caused by the buildup of plaque on your teeth and gums, which leads to inflammation of the gum tissues. Gingivitis is usually painless, but if ignored, it can cause red, swollen, and bleeding gums. Over time, this condition can progress to more severe gum disease, which can lead to tooth loss.
Gingivitis can affect anyone, but certain factors increase the risk. If you want to prevent gingivitis and protect your oral health, it’s essential to take proactive measures. Fortunately, there are many ways to prevent this common dental problem and keep your gums healthy for years to come.
Gingivitis is extremely common — clinical research shows plaque‑induced gingivitis affected up to 100 %of adult participants in a dental clinic sample, underscoring how pervasive the condition can be without preventive care.
Brushing After Meals: A Simple and Effective Habit
One of the simplest yet most effective ways to prevent gingivitis is brushing your teeth after every meal. It’s easy to overlook brushing after meals, but doing so helps prevent food particles and plaque from lingering on your teeth and gums. Plaque is a sticky film of bacteria that forms on your teeth after eating. If not removed promptly, plaque can irritate your gums, leading to inflammation and gingivitis.
"Brushing after meals is one of the most effective ways to prevent plaque buildup, which is the leading cause of gingivitis. It may seem like a small habit, but it goes a long way toward protecting your gums."
— Dr. Goli Ariafar, DDS
If you can’t brush immediately after eating, rinse your mouth with water or chew sugar-free gum to help remove food particles and stimulate saliva production, which naturally helps clean your mouth.
Epidemiological evidence confirms that plaque accumulation is a key risk factor for gingivitis — reducing plaque through proper brushing significantly lowers your risk.
Flossing: The Forgotten Hero of Gum Health
While brushing is essential, it’s not enough on its own. Flossing is equally important in preventing gingivitis. It removes food particles and plaque from between your teeth and along the gumline — areas that your toothbrush can’t reach effectively. Flossing helps reduce plaque buildup, which is the main contributor to gingivitis.
Research Insight:
Studies of pediatric populations show that inadequate hygiene behaviour, including poor brushing and flossing, is strongly linked with gingivitis prevalence.
"Flossing is a critical part of any oral hygiene routine. It helps prevent plaque buildup in areas your toothbrush can’t reach, significantly reducing the risk of gingivitis."
— Dr. James C.H. Ko, DDS
Flossing can be done at any time of day, but it’s best to floss before brushing so you can remove the particles and plaque between your teeth and allow your toothbrush to clean the surfaces more effectively.
Diet: What You Eat Plays a Role in Gum Health
What you eat affects more than just your waistline; it also plays a significant role in your gum health. A balanced diet that includes vitamins and minerals such as vitamin C, calcium, and iron is essential for maintaining strong, healthy gums. These nutrients help your body’s immune system resist gum infections like gingivitis.
Foods to Include
- Vitamin C-rich foods, such as citrus fruits, strawberries, and leafy greens, help keep your gums healthy.
- Calcium-rich foods: Dairy products, leafy vegetables, and fortified plant-based milks help strengthen your teeth and gums.
- Iron: Foods like spinach, beans, and lentils support healthy gums by boosting your immune system.
"A healthy diet is just as important as good oral hygiene when it comes to preventing gingivitis. Foods that support your immune system and provide essential vitamins help keep your gums strong and resistant to disease."
— Dr. Rob Eisen, DDS
It’s also crucial to avoid excessive consumption of sugary and acidic foods, as these can contribute to plaque buildup and lead to gingivitis. Drinking plenty of water throughout the day helps wash away food particles and bacteria that can cause gum inflammation.

Quit Smoking and Using Tobacco Products
Tobacco use is one of the leading causes of gum disease, including gingivitis. Smoking and chewing tobacco reduce blood flow to your gums, which weakens your immune system and makes it harder for your body to fight infections, including gum disease.
According to the Canadian Dental Association, smokers are at a significantly higher risk of developing gingivitis and periodontal disease compared to non-smokers. In fact, research shows that smoking doubles the likelihood of developing gum disease.
"If you're trying to avoid gingivitis and protect your overall oral health, quitting tobacco should be a top priority. Tobacco weakens your gums, making them more susceptible to infection."
— Dr. Goli Ariafar, DDS
If you are a smoker, seeking help to quit can greatly reduce your risk of gingivitis and improve your overall gum health. Talk to your dentist about resources available to help you quit.
Never Skip Your Dental Checkups
Regular visits to your dentist are essential in preventing gingivitis. Your dentist can detect early signs of gum disease before it becomes a serious issue. During routine checkups, your dentist will perform a thorough cleaning to remove plaque and tartar buildup, which can lead to gingivitis if left untreated.
A routine exam typically includes a professional cleaning, an oral cancer screening, and a detailed examination of your gums and teeth to detect any abnormalities. If gingivitis is found, your dentist will provide treatment options to restore your gum health.
The Bottom Line: Prevention is Key
The best way to avoid gingivitis is to combine responsible dental hygiene with regular dental checkups. By brushing and flossing regularly, maintaining a balanced diet, avoiding tobacco products, and keeping your dental appointments, you can greatly reduce your risk of developing gingivitis and other forms of gum disease.
If it’s been a while since your last checkup, call today and schedule an appointment. Early detection and treatment are the best ways to protect your gums and keep your smile healthy for years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions About Gingivitis
How do I know if I have gingivitis?
Common signs of gingivitis include red, swollen gums that bleed when you brush or floss. If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s important to schedule an appointment with your dentist.
Can gingivitis be reversed?
Yes, gingivitis can often be reversed with proper brushing, flossing, and professional dental cleanings. Early intervention is key to preventing the condition from progressing.
Is gingivitis contagious?
No, gingivitis is not contagious. It is caused by the buildup of plaque and bacteria on the gums, not by direct contact with an infected person.
How long does it take to treat gingivitis?
The treatment for gingivitis can take a few days to a few weeks, depending on the severity. With proper oral care and professional treatment, your gums should begin to heal quickly.

